A
- abugida
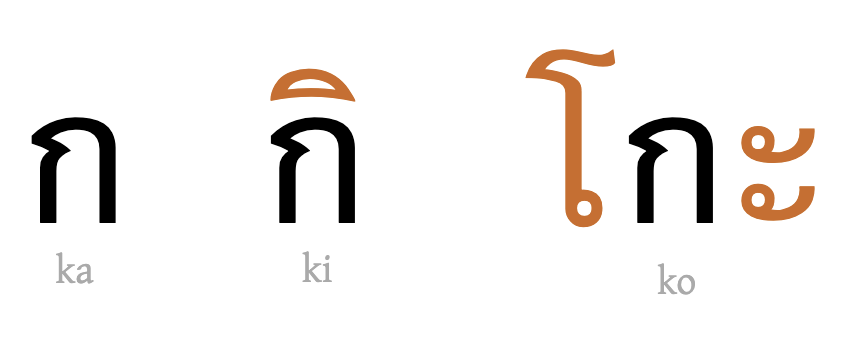
- A writing system in which consonant letters have an inherent vowel. Other post-consonant vowel sounds are indicated by associating one or more letters or marks with the consonant and they override the inherent vowel. These are often referred to as vowel signs. Most abugidas derive from the ancient Brahmi script. The term “abugida” is derived from the first four letters of the Ethiopic script in the Semitic order: alf, bet, gaml, dant. (See also Section 6.1, Writing Systems. Note: In resources on the r12a site, modern Ethiopic is regarded as a featural syllabary, rather than an abugida, since it doesn't require a sequence of code points to represent a CV syllable.)
- abjad
- A writing system in which consonant sounds are written but short vowel sounds are usually not. Usually, diacritics can be used represent the missing vowels in order to disambiguate words or help in education, but they are not used in normal text. Abjads include the Arabic and Hebrew scripts. The term “abjad” is derived from the first four letters of the traditional order of the Arabic script: alef, beh, jeem, dal. (See also Section 6.1, Writing Systems.)

- alphabet
- A writing system in which both consonants and vowels are indicated. Vowels may be indicated using dedicated letters or combining marks. For example, several orthographies using the Arabic script always show all diacritics, making them alphabetic in nature. The term “alphabet” is derived from the first two letters of the Greek script: alpha, beta. (See also Section 6.1, Writing Systems.)





