Ornate parentheses
These are traditional Arabic punctuation marks, and are commonly used in not only Arabic text but may also appear in text written in other scripts, such as N'Ko and Mandaic.
Updated 3 November, 2023
In general, the code points in the Unicode blocks Arabic Presentation Forms-A and Arabic Presentation Forms-B should not be used for ordinary text. Those code points are provided for compatibility with legacy code pages, and have (compatibility) character decomposition mappings. Normally, Arabic text should be written with code points from the main Arabic block and its extensions; positional forms are dealt with by the font and rendering algorithms.
However, there are some exceptions to this rule, and we attempt to list those in this page. These characters are not included in the Unicode repertoire for compatibility but may be used in Arabic texts, in their own right. They normally don't have character decomposition mappings. For descriptions of use see Chapter 9 of the Unicode Standard (pages 398-400 in version 15). Some of these characters may find more use with one language than with another in contemporary text.
These are traditional Arabic punctuation marks, and are commonly used in not only Arabic text but may also appear in text written in other scripts, such as N'Ko and Mandaic.
A number of word ligatures are used in texts as honorifics. (The main Arabic block has 4 related code points which are combining marks.)
 U+FD40 ARABIC LIGATURE RAHIMAHU ALLAAH
U+FD40 ARABIC LIGATURE RAHIMAHU ALLAAH
 U+FD41 ARABIC LIGATURE RADI ALLAAHU ANH
U+FD41 ARABIC LIGATURE RADI ALLAAHU ANH
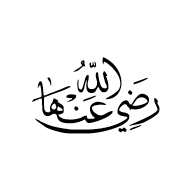 U+FD42 ARABIC LIGATURE RADI ALLAAHU ANHAA
U+FD42 ARABIC LIGATURE RADI ALLAAHU ANHAA
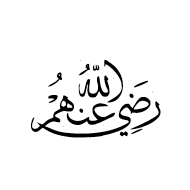 U+FD43 ARABIC LIGATURE RADI ALLAAHU ANHUM
U+FD43 ARABIC LIGATURE RADI ALLAAHU ANHUM
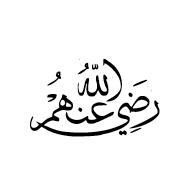 U+FD44 ARABIC LIGATURE RADI ALLAAHU ANHUMAA
U+FD44 ARABIC LIGATURE RADI ALLAAHU ANHUMAA
 U+FD45 ARABIC LIGATURE RADI ALLAAHU ANHUNNA
U+FD45 ARABIC LIGATURE RADI ALLAAHU ANHUNNA
 U+FD46 ARABIC LIGATURE SALLALLAAHU ALAYHI WA-AALIH
U+FD46 ARABIC LIGATURE SALLALLAAHU ALAYHI WA-AALIH
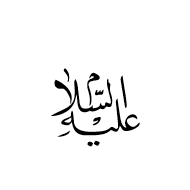 U+FD47 ARABIC LIGATURE ALAYHI AS-SALAAM
U+FD47 ARABIC LIGATURE ALAYHI AS-SALAAM
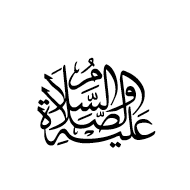 U+FD4A ARABIC LIGATURE ALAYHI AS-SALAATU WAS-SALAAM
U+FD4A ARABIC LIGATURE ALAYHI AS-SALAATU WAS-SALAAM
 U+FD4B ARABIC LIGATURE QUDDISA SIRRAH
U+FD4B ARABIC LIGATURE QUDDISA SIRRAH
 U+FD4C ARABIC LIGATURE SALLALLAHU ALAYHI WAAALIHEE WA-SALLAM
U+FD4C ARABIC LIGATURE SALLALLAHU ALAYHI WAAALIHEE WA-SALLAM
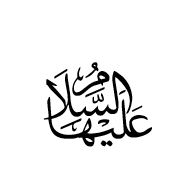 U+FD4D ARABIC LIGATURE ALAYHAA AS-SALAAM
U+FD4D ARABIC LIGATURE ALAYHAA AS-SALAAM
 U+FD4E ARABIC LIGATURE TABAARAKA WA-TAAALAA
U+FD4E ARABIC LIGATURE TABAARAKA WA-TAAALAA
 U+FD4F ARABIC LIGATURE RAHIMAHUM ALLAAH
U+FD4F ARABIC LIGATURE RAHIMAHUM ALLAAH
 U+FDCF ARABIC LIGATURE SALAAMUHU ALAYNAA
U+FDCF ARABIC LIGATURE SALAAMUHU ALAYNAA
 U+FDFD ARABIC LIGATURE BISMILLAH AR-RAHMAN AR-RAHEEM
U+FDFD ARABIC LIGATURE BISMILLAH AR-RAHMAN AR-RAHEEM
The following code points may sometimes also be used as regular characters, although they do have character decomposition mappings.
 U+FDF2 ARABIC LIGATURE ALLAH ISOLATED FORM
U+FDF2 ARABIC LIGATURE ALLAH ISOLATED FORM
Decomposition mapping: الله
 U+FDF4 ARABIC LIGATURE MOHAMMAD ISOLATED FORM
U+FDF4 ARABIC LIGATURE MOHAMMAD ISOLATED FORM
Decomposition mapping: محمد
 U+FDFA ARABIC LIGATURE SALLALLAHOU ALAYHE WASALLAM
U+FDFA ARABIC LIGATURE SALLALLAHOU ALAYHE WASALLAM
Decomposition mapping: صلى الله عليه وسلم
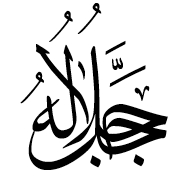 U+FDFB ARABIC LIGATURE JALLAJALALOUHOU
U+FDFB ARABIC LIGATURE JALLAJALALOUHOU
Decomposition mapping: جل جلاله
In educational materials there is sometimes a need to show pictures of the dots and marks used to distinguish Arabic characters, particularly the ijam. These code points provide for that use case. They are never used as combining marks, nor in composition with Arabic letter forms, but are simply symbols.
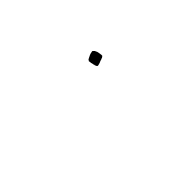 U+FBB2 ARABIC SYMBOL DOT ABOVE
U+FBB2 ARABIC SYMBOL DOT ABOVE
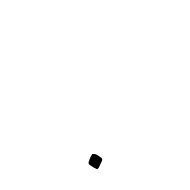 U+FBB3 ARABIC SYMBOL DOT BELOW
U+FBB3 ARABIC SYMBOL DOT BELOW
 U+FBB4 ARABIC SYMBOL TWO DOTS ABOVE
U+FBB4 ARABIC SYMBOL TWO DOTS ABOVE
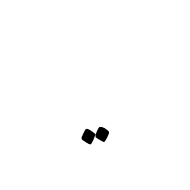 U+FBB5 ARABIC SYMBOL TWO DOTS BELOW
U+FBB5 ARABIC SYMBOL TWO DOTS BELOW
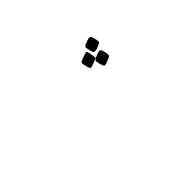 U+FBB6 ARABIC SYMBOL THREE DOTS ABOVE
U+FBB6 ARABIC SYMBOL THREE DOTS ABOVE
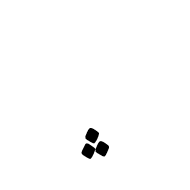 U+FBB7 ARABIC SYMBOL THREE DOTS BELOW
U+FBB7 ARABIC SYMBOL THREE DOTS BELOW
The Unicode Consortium. The Unicode Standard, Version 15.0.0, (Mountain View, CA: The Unicode Consortium, 2022. ISBN 978-1-936213-32-0)