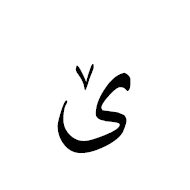This page lists a number of Arabic script characters and character sequences that look the same, given the right font, but that may need to be used with caution because the alternative forms differ in usage and meaning.
Ijam, tashkil, hamza
Chapter 9 of the Unicode Standard makes an important distinction between ijam and tashkil diacritics.
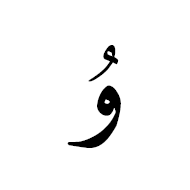
إِعْجَام An ijam is a diacritic in the Arabic script that is considered to be an integral part of a basic letter form, such as the dots in
ث [U+062B ARABIC LETTER THEH],
pronounced θ. Unicode encodes letter+ijam combinations as atomic characters, which are never given equivalent decompositions in the standard. Ijam generally take the form of one-, two-, three- or four-dot markings above or below the basic letter skeleton, although other diacritic forms occur, especially in extensions of the Arabic script in Central and South Asia and in Africa. For example, ۈ [U+06C8 ARABIC LETTER YU] is a letter with ijam that represents the vowel y in the Uighur orthography.
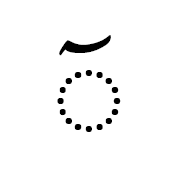
تَشْكِيل A tashkil is an Arabic script mark that indicates vocalization of text or other types of phonetic guide that indicate pronunciation, such as in
ثَ [U+062B ARABIC LETTER THEH + U+064E ARABIC FATHA],
pronounced θa. These include several subtypes: harakat (short vowel marks), tanwin (postnasalized or long vowel marks), shaddah (consonant gemination mark), and sukun (to mark lack of a following vowel). A basic Arabic letter plus any of these types of marks is never encoded as an atomic, precomposed character, but must always be represented as a sequence of letter plus a separate combining mark. For example,
هٰ [U+0647 ARABIC LETTER HEH + U+0670 ARABIC LETTER SUPERSCRIPT ALEF]
pronounced ha, is an example of a letter plus tashkil combination in Arabic (cf. use of that diacitic as part of a precomposed character in Uighur).
This distinction between using a character with ijam instead of combining a letter with a tashkil becomes important when choosing which Unicode characters to use because (as can be seen in the examples above) the visual forms can be identical. Using the wrong character can change the meaning of the text, affecting the results of text search, font rendering, text to speech, etc.
There are, however, some very common combinations of diacritic and base that can be represented using precomposed characters or decomposed sequences that are canonically equivalent. For those the standard encourages the use of the precomposed form, but the fact that the forms are canonically equivalent removes concerns about changes in meaning.
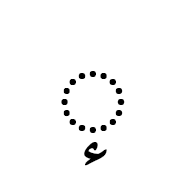
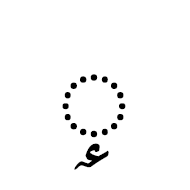
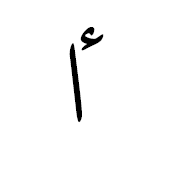
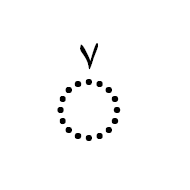
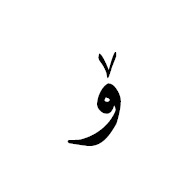
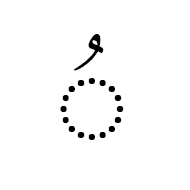
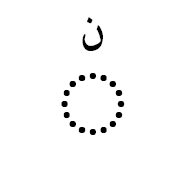
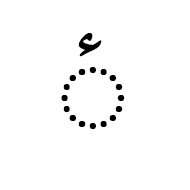
هَمْزة The hamza is another Arabic script mark that may be precomposed with a letter in some code points, or attached to a letter as a combining mark in others. It is not regarded as a tashkil. It is typically used for the Arabic language to represent the glottal stop, or in Persian or Urdu as the ezafe, but it has other uses in extended orthographies. For example, it represents a vowel in Kashmiri, and as such can appear above a number of letters for which there are no precomposed alternatives.
The Arabic letter yeh is associated with some special, idiosynchratic rules when it comes to the hamza.
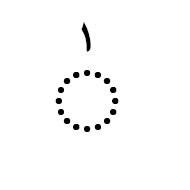
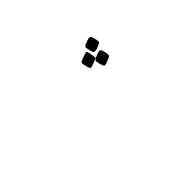
 when you want no dots in any positional form.
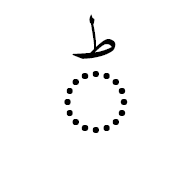
when you want no dots in any positional form.  when you do want dots in all positional forms.
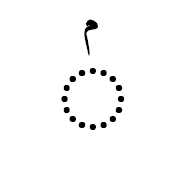
when you do want dots in all positional forms.  when you want dots in initial & medial positional forms only.
when you want dots in initial & medial positional forms only.